Which Of The Following Is An Economic Factor Related To An Asset's Service Life?
What is Economical Life?
Economical life refers to the length of time an asset is expected to be useful to the owner. It is also called useful life or depreciable life. The measure out of an nugget's usefulness is how profitable it is to keep – in other words, how long an nugget generates more income than information technology costs to maintain and operate.
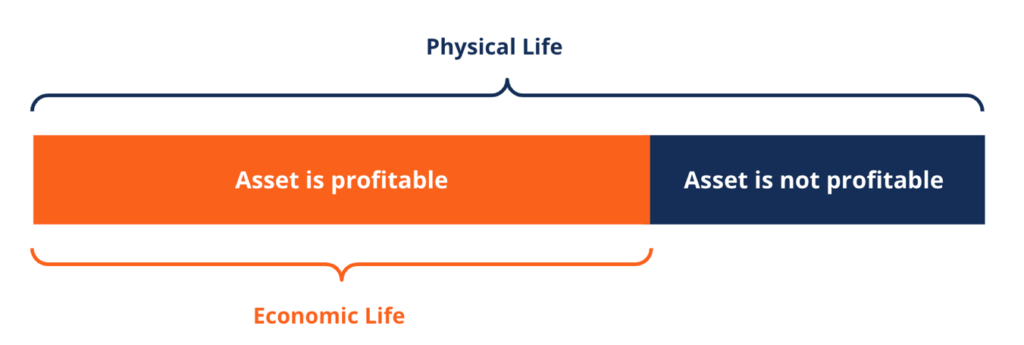
When calculating economic life, it is normally assumed that the asset will exist operated at a normal level of usage and with preventative maintenance. An asset's economical life is not always the same length as its physical life. An asset could even so exist functioning every bit it is supposed to, but not considered economically useful. Because economic life is an interpretation, an nugget's physical life can exceed its economic life or vice versa. This is also the case when new technological innovations make one-time technology obsolete.
Summary
- Economical life is the length of time an asset is expected to be useful to the owner.
- Assumptions when calculating economic life are that the nugget will exist operated at a normal level of usage and with preventative maintenance.
- Economic life can exist reduced or concluded past asset wear and impairment, asset obsolescence, and changes in business operations.
Determining an Asset's Economical Life
In some cases, the owner or visitor volition designate an arbitrary number of years to define an asset's economical life. To approximate the number, owners must consider the nugget's net present value (NPV) , internal rate of return (IRR), and return on investment (ROI) .
An asset'due south economic life can exist reduced or concluded by several factors. Asset habiliment, deposition, or harm reduces an asset'south economical life. It lowers asset performance and also raises the costs needed for maintenance and repair.
Asset obsolescence occurs when new innovations and technology supplant electric current ones. It reduces economical life if it raises maintenance costs, and sometimes information technology ends an asset's economic life because it renders the asset'southward operation inefficient compared to current alternatives.
For case, the widespread employ of e-mail replaced faxing and concluded the economic life of many fax machines. Lastly, changes in business operations or business organization models reduce economic life if information technology affects the value certain assets can evangelize to a business.
How is Economic Life Used?
The concept of economic life is useful for accountants of a company, operators of the asset, and visitor decision-makers. For accounting purposes, economical life is used every bit the time catamenia in which depreciation is charged against an asset. Companies utilise information technology to classify depreciation expenses charged for the use of the asset.
Effectively managing avails is the fundamental to economic life. It is also 1 of the important considerations of a company'due south controlling process to buy new assets or supersede current assets.
By studying and determining when machines, equipment, and other technologies become less effective and uneconomic, companies can finer plan to replace such avails with new ones at appropriate intervals. The right planning volition reduce maintenance and other overhead costs.
Applied Instance
For case, in farm businesses machinery and equipment are major cost items. Owners that brand smart decisions about how to learn mechanism, how to properly maintain the machinery, when to trade in sometime machinery, and how much capital to invest, can help to maximize the benefit while reducing the total costs. The economic life of each motorcar will betoken the number of years over which costs will be allocated.
In such a example, it is usually shorter than the motorcar's actual catamenia of usefulness, as most farmers trade machines for newer ones before the old machine is completely worn out. For most subcontract machines, a 10- to 12-year economical life is a adept dominion of thumb and 15 years for tractors. At the end of a machine's economic life, the farmer tin can either merchandise it in, sell it, or dispose of it.
Salvage value, the judge of the sale value of the motorcar at the end of its economic life, is also always specified. It is the monetary amount the farmer tin expect to receive if they merchandise in the machine for a newer 1 or if they sell the automobile outright at the end of its economical life. The salvage value can be zero if the machine is being kept until information technology's worn out completely.
More Resource
CFI is the official provider of the global Commercial Banking & Credit Annotator (CBCA)™ certification program, designed to help anyone become a world-class financial analyst. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources beneath volition exist useful:
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
- Maintenance Expenses
- Overheads
- PP&East (Property, Plant, & Equipment)
Which Of The Following Is An Economic Factor Related To An Asset's Service Life?,
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/accounting/economic-life/
Posted by: mcfarrentreasking.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Is An Economic Factor Related To An Asset's Service Life?"
Post a Comment